Convex lenses
Variant i Interactive tutorial lecture Other Variants Dynamics first
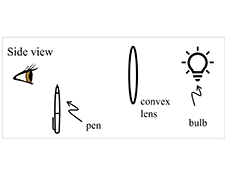
Students use parallax to find the location of an image produced by a convex lens. Their observations help them infer the paths of various rays and motive the idea of focal points.
Topics Waves and optics / Geometrical optics: representations, geometric optics, images, lenses, light (or shadow), parallax, and ray tracing
Materials
Materials by the UW team
- Clicker Questions Only

- Instructor Guide

- Pretest


- Pretest for LMS


- Exam Questions


- Equipment List

Tutorial details
Section I: Parallax
Students are introduced to the concept of parallax by holding up two fingers, closing one eye, and moving their head from side to side. In Questions B-D, students generalize their observations to establish a rule to determine the relative distances of two objects.
Section II: Application of parallax to lenses
This section involves a series of video demonstrations. Students use parallax to determine the location of the image of a distant bulb produced by a converging lens. This establishes that the image of an object does not have the same location as the object itself and is not located on the surface of the lens.
Section III: Light rays and lenses
Students use their observations to sketch the path of several light rays to develop a functional understanding of the focal point of a convex lens.
Section IV: Principal rays
By considering the reversibility of the paths of light, students are led to recognize two rays that are useful in determining the location of the image of an object: (1) a ray that arrives at a lens parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point on the other side of the lens and (2) a ray that passes through one of the focal points emerges parallel to the principal axis. The term principal ray is then introduced, and they consider the third principal ray, which passes through the center of the lens.
Section V: Supplement
Students use principal rays to find the image locations for two objects.
For instruction tips, login or register as a verified educator to see the Instructor Guide.
Prerequisites
Prerequisite tutorials
The Light and shadow tutorial is a prerequisite to Convex lenses.
Other prerequisites
Students need not have previously studied lenses. However, it may be useful for students to have worked through the tutorial Light and Shadow in order to establish that light moves (1) in straight lines and (2) outward in all directions from each point on an object.
Resources and Links
https://youtu.be/KakrtyrYtjk, https://youtu.be/RJcCYALhtlQ, https://youtu.be/lQGgHD0lo78
Research
- F. Goldberg and L. McDermott, An investigation of student understanding of the real image formed by a converging lens or concave mirror, Am. J. Phys. 55 (2), 108 (1987).
Coming Soon! We hope to release the discussion section on each tutorial soon.

