Light and shadow
Variant i Interactive tutorial lecture Other Variants Dynamics first
Observations motivate a model for geometrical optics: (1) light moves outward in straight lines from point sources and (2) extended sources act as collections of point sources.
Topics Waves and optics / Geometrical optics: limits, models, representations, geometric optics, geometry, light (or shadow), and point vs. extended sources
Materials
Materials by the UW team
- Clicker Questions Only

- Instructor Guide

- Pretest


- Pretest for LMS


- Exam Questions


- Equipment List

Tutorial details
There are many observations throughout this tutorial. It is important that students make predictions before viewing the corresponding demonstrations.
Section I: Point sources of light
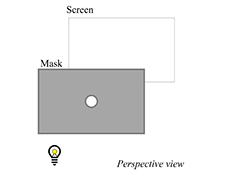
In Questions A-D, students predict what will appear on the screen when a mask with a circular hole is placed between a bulb and the screen. They consider how moving the bulb or introducing a second bulb would affect the appearance of the screen, which builds to the idea that light travels in straight lines.
In Questions E-G, students consider the effect of replacing the circular hole with a triangular one as well as the impact of moving the bulb farther and farther away from the mask.
Section II: Extended sources of light
In Questions A-C, the circular hole is again used and bulbs are continually added in a vertical stack. This leads to the long filament bulb, where students recognize that it can be treated as a collection of many closely-spaced bulbs.
Questions D-F involve variations on the experiment with the long filament bulb. Students then consider a frosted bulb in Question G.
Section III: Shadows
In this section, students apply their understanding in the complementary context of shadows.
Section IV: Supplement
Students make quantitative predictions about the size of the image produced by light from a small bulb passing through a small hole. They also examine the effect of halving the diameter of the hole in the mask for both the small bulb and a long-filament bulb.
For instruction tips, login or register as a verified educator to see the Instructor Guide.
Prerequisites
None.
Equipment
Special Instructions
If, after the interactive tutorial lecture, students need access to the images showing the results of experiments in this tutorial, they can find them at this link: [ ]
List
- tutorial instructor slides
- tutorial student slides or worksheet
Research
- K. Wosilait, P. Heron, P. Shaffer, and L. McDermott, Development and assessment of a research-based tutorial on light and shadow, Am. J. Phys. 66 (10), 906 (1998).
Coming Soon! We hope to release the discussion section on each tutorial soon.

