Developed by: Jeffrey T. Morgan, Michael C. Wittmann, Eleanor C. Sayre, Katrina E. Black





middle schoolhigh schoolintro collegeinter-mediateupper levelgrad school other

conceptual







Overview
What? Tutorials for a course introducing non-science majors to the basic ideas of quantum mechanics using minimal mathematics. Uses simplified models to help students understand spectroscopy, building simple molecules, and tunneling.
Topic outline
Seeing the same things as other people
Waves passing through
Analogies connecting light and waves
Doing impossible things
Probability
Energy
Energy and probability
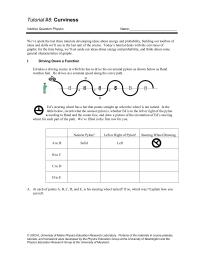
Curviness
Physically possible wavefunctions
Bound states and more impossible things
Excited States
Modeling Molecules
Tunneling – A quantum mechanical consequence
Modeling Radioactivity
Student skills developed
- Conceptual understanding
- Making real-world connections
- Metacognition
- Using multiple representations
Instructor effort required
- High
Resources required
- TAs / LAs
- Advanced lab equipment
- Tables for group work
Resources
Teaching Materials
You can download all course materials including tutorials, quizzes, and movies for free from the developer's website. You can download a sample tutorial from PhysPort.
Research
This is the third highest level of research validation, corresponding to:
- at least 1 of the "based on" categories
- at least 1 of the "demonstrated to improve" categories
- at least 1 of the "studied using" categories
Research Validation Summary
Based on Research Into:
- theories of how students learn
- student ideas about specific topics
Demonstrated to Improve:
- conceptual understanding
- problem-solving skills
- lab skills
- beliefs and attitudes
- attendance
- retention of students
- success of underrepresented groups
- performance in subsequent classes
Studied using:
- cycle of research and redevelopment
- student interviews
- classroom observations
- analysis of written work
- research at multiple institutions
- research by multiple groups
- peer-reviewed publication
References
- M. Wittmann and J. Morgan, Foregrounding epistemology and everyday intuitions in a quantum physics course for nonscience majors, Phys. Rev. Phys. Educ. Res. 16 (2), 020159 (2020).
- M. Wittmann, J. Morgan, and L. Bao, Addressing Student Models of Energy Loss in Quantum Tunneling, Eur. J. Phys. 26 (6), 939 (2005).
- M. Wittmann, J. Morgan, and R. Feeley, Laboratory-tutorial activities for teaching probability, Phys. Rev. ST Phys. Educ. Res. 2 (2), (2006).